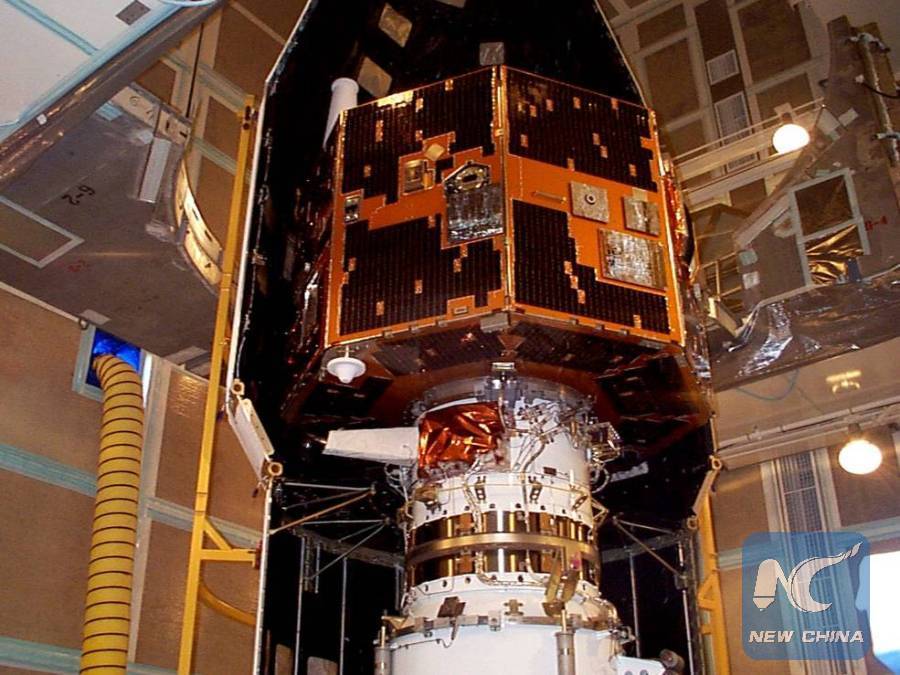

Pic shows the IMAGE spacecraft undergoing launch preparations in early 2000. (Credits: NASA)
WASHINGTON, Jan. 29 (Xinhua) -- U.S. space agency NASA said Monday that it's attempting to contact a satellite it lost more than a decade ago, after it was discovered possibly still alive by an amateur astronomer earlier this month.
"We are attempting to contact the IMAGE satellite via the Deep Space Network after an amateur astronomer reported making contact in mid-January," NASA tweeted.
NASA's tweet on the IMAGE satellite.
The satellite, known as Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration (IMAGE), was launched on March 25, 2000, and contact was unexpectedly lost on Dec. 18, 2005.
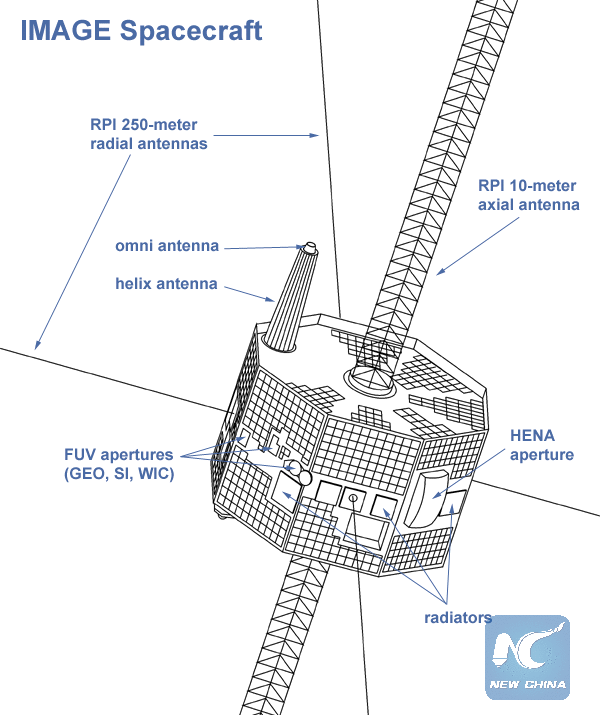
Diagram of NASA's IMAGE spacecraft. (Credits: NASA)
It was the first satellite mission dedicated to imaging the Earth's magnetosphere, the region of space controlled by the Earth's magnetic field and containing extremely tenuous plasmas of both solar and terrestrial origin.
At that time, NASA said the most likely explanation of the failure was due to an induced "instant trip" of the solid-state power controller supplying power to the transponder.

NASA's tweet on the IMAGE satellite.
Earlier this month, an amateur astronomer called Scott Tilley wrote on his blog that he picked up a signal from a satellite labeled "2000-017A, 26113" which he knew corresponded to the IMAGE satellite.
NASA said it has acquired time on the Deep Space Network to focus on the source and determine whether the signal is indeed IMAGE.
"This process must take into consideration the vintage nature of the spacecraft, and includes locating appropriate software and commands to potentially operate the mission," the U.S. space agency added.
If IMAGE is revived, its orbit will be well positioned to monitor Earth's northern auroral zone, Patricia Reiff, a space plasma physicist at Rice University who was also a co-investigator on the mission, told Science Magazine.
"It is really invaluable for now-casting space weather and really understanding the global response of the magnetosphere to solar storms," Reiff added.

